LeetCode记录
地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/ 记录下刷题记录和思路吧
73. 矩阵置零 2021年3月21日
难度中等460收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
给定一个 *m* x *n* 的矩阵,如果一个元素为 0 ,则将其所在行和列的所有元素都设为 0 。请使用 原地 算法。
进阶:
- 一个直观的解决方案是使用
O(*m**n*)的额外空间,但这并不是一个好的解决方案。 - 一个简单的改进方案是使用
O(*m* + *n*)的额外空间,但这仍然不是最好的解决方案。 - 你能想出一个仅使用常量空间的解决方案吗?
示例 1:
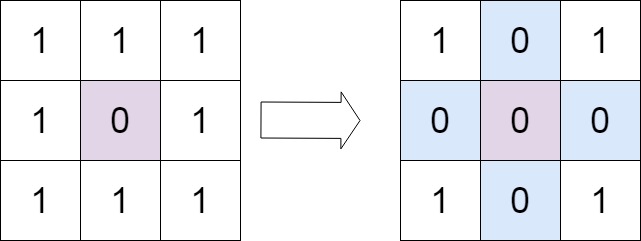
输入:matrix = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]] |
示例 2:
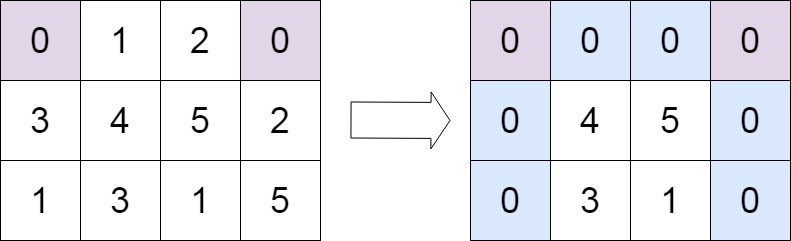
输入:matrix = [[0,1,2,0],[3,4,5,2],[1,3,1,5]] |
提示:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[0].length1 <= m, n <= 200-231 <= matrix[i][j] <= 231 - 1
2021年3月21日 每日一题 完成
Java代码
class Solution { |
解题思路
先第一遍遍历 用横竖2个数组记录下 对应序号是否为0,第二遍遍历,把对应行号或者列号上的数字清0 来解决问题.
3. 无重复字符的最长子串 2021年3月21日
难度中等5176收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
给定一个字符串,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例 1:
输入: s = "abcabcbb" |
示例 2:
输入: s = "bbbbb" |
示例 3:
输入: s = "pwwkew" |
示例 4:
输入: s = "" |
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 5 * 104s由英文字母、数字、符号和空格组成
2021年3月21日 完成
Java
class Solution { |
解题思路
移动窗户的想法,先记录下每个元素的坐标,如果有重复,就把左边的start向右移动,然后遍历的右坐标继续增加,同时记录下最长的不重复的值,关键的点是左边的start是要取历史以来最大值.
191. 位1的个数 2021年3月22日
难度简单329收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
编写一个函数,输入是一个无符号整数(以二进制串的形式),返回其二进制表达式中数字位数为 ‘1’ 的个数(也被称为汉明重量)。
提示:
- 请注意,在某些语言(如 Java)中,没有无符号整数类型。在这种情况下,输入和输出都将被指定为有符号整数类型,并且不应影响您的实现,因为无论整数是有符号的还是无符号的,其内部的二进制表示形式都是相同的。
- 在 Java 中,编译器使用二进制补码记法来表示有符号整数。因此,在上面的 示例 3 中,输入表示有符号整数
-3。
示例 1:
输入:00000000000000000000000000001011 |
示例 2:
输入:00000000000000000000000010000000 |
示例 3:
输入:11111111111111111111111111111101 |
提示:
- 输入必须是长度为
32的 二进制串 。
2021年3月22日 每日一题 完成
Java代码
public class Solution { |
解题思路
通过位操作,并向右移位来判断,个数自加.
341. 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器 2021年3月23日
难度中等270收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
给你一个嵌套的整型列表。请你设计一个迭代器,使其能够遍历这个整型列表中的所有整数。
列表中的每一项或者为一个整数,或者是另一个列表。其中列表的元素也可能是整数或是其他列表。
示例 1:
输入: [[1,1],2,[1,1]] |
示例 2:
输入: [1,[4,[6]]] |
2021年3月23日 每日一题完成
Java
/** |
解题思路
主要是变量添加,查看是否是数组,如果是的话 递归操作,直到不是数组位置,层层递归拿到所有元素,再直接使用元素遍历.
7. 整数反转 2021年3月23日
难度简单2627收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
给你一个 32 位的有符号整数 x ,返回将 x 中的数字部分反转后的结果。
如果反转后整数超过 32 位的有符号整数的范围 [−231, 231 − 1] ,就返回 0。
假设环境不允许存储 64 位整数(有符号或无符号)。
示例 1:
输入:x = 123 |
示例 2:
输入:x = -123 |
示例 3:
输入:x = 120 |
示例 4:
输入:x = 0 |
提示:
-231 <= x <= 231 - 1
2021年3月23日 完成
Java
class Solution { |
解题思路
先记录下数字的正负,根据%10的操作取出每个位同时 新的数字去*10加上,要注意边界的问题,将反转后的数字返回.
456. 132模式 2021年3月24日
难度中等406收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中共有 n 个整数。132 模式的子序列 由三个整数 nums[i]、nums[j] 和 nums[k] 组成,并同时满足:i < j < k 和 nums[i] < nums[k] < nums[j] 。
如果 nums 中存在 132 模式的子序列 ,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
进阶:很容易想到时间复杂度为 O(n^2) 的解决方案,你可以设计一个时间复杂度为 O(n logn) 或 O(n) 的解决方案吗?
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3,4] |
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,1,4,2] |
示例 3:
输入:nums = [-1,3,2,0] |
提示:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 104-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
Java 循环方式
public boolean find132pattern(int[] nums) { |
解题思路
循环每一个数i,再从最后开始向i查找,找到2个比num[i]大的数字 切第二个找到的数字比第一个找到的数字大就说明对.就是数i,j,k 先找i然后找k然后最后找到j成立.
Java 栈的实现
public boolean find132pattern(int[] nums) { |
解题思路
时间复杂度更低,从尾节点找起,一个栈 数字只能递减 这样的话 记录下最大的出栈的数字 因为出栈 最大的数字肯定为除栈底的那个数第二大的数字,然后继续循环 直到找到一个数比出栈的第二大的数字小的数就说明成立.关键点max = stack.pop(); 因为数字是主键递减的 所有最后出栈的数字肯定是最大的 所以 不需要加 max = Math.max(stack.pop(),max);利用了栈的结构 巧妙的取第二大的数字 一次遍历完成.今天的算法题思路还是挺好的,学习到了.
82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II 2021年3月25日
难度中等526收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
存在一个按升序排列的链表,给你这个链表的头节点 head ,请你删除链表中所有存在数字重复情况的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现 的数字。
返回同样按升序排列的结果链表。
示例 1:
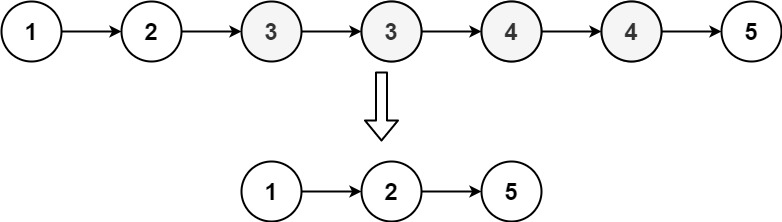
输入:head = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5] |
示例 2:
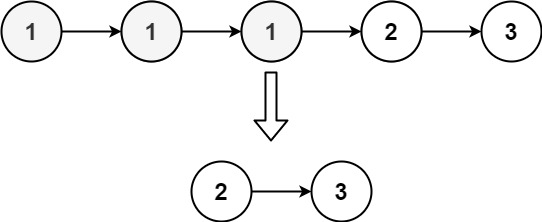
输入:head = [1,1,1,2,3] |
提示:
- 链表中节点数目在范围
[0, 300]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100- 题目数据保证链表已经按升序排列
Java
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { |
解题思路
循环变量,找到每个节点,查询和下一个节点比较如果不一致,修改辨识符,就是连续遍历过程中连续遍历不一样2次的保存到新的节点上,第一次多了几次判断去首节点为空判断.哆嗦了很多.看了别人的解题思路,学习了链表的通用解法.
Java 优化
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { |
解题思路
新建一个空节点,后续去返回这个节点之后的数据 判断当前值和后一节点值一直的情况下去向后移动坐标,以做到过滤的作用.
注意 整体要考虑最后一个节点的问题 还有节点个数小于等于1的情况
83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 2021年3月26日
难度简单515收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
存在一个按升序排列的链表,给你这个链表的头节点 head ,请你删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素 只出现一次 。
返回同样按升序排列的结果链表。
示例 1:
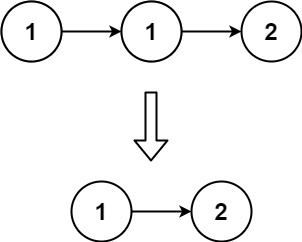
输入:head = [1,1,2] |
示例 2:
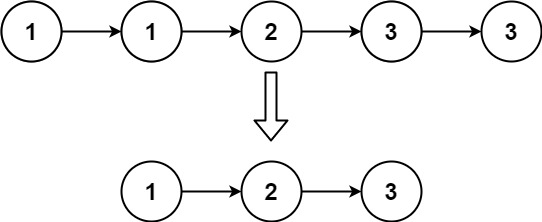
输入:head = [1,1,2,3,3] |
提示:
- 链表中节点数目在范围
[0, 300]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100- 题目数据保证链表已经按升序排列
Java
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { |
解题思路
根据昨天做的删除元素2,遍历整个链表 判断只有值不一样的情况下再去新建节点 最后返回首节点的next 要注意为空和只有一个元素的特殊情况.
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表 2021年3月26日
难度简单198收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL |
限制:
0 <= 节点个数 <= 5000 |
注意:本题与主站 206 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
Java解法1
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { |
解题思路
利用栈结构,先进后出,先遍历出所有的节点,再正向生成反转后的列表,相当于遍历2次返回列表.
Java解法2
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { |
解题思路
链表1->2->3->4->null 要转换为4->3->2->1->null 但是遍历是正向遍历的,就是链表是反向生成的从最开始的1->null开始生成.用新建的节点变为上个节点的next 做到一次循环完成链表的反转.
Java递归
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { |
解题思路
关键点
head.next.next = head; |
目前反转的k位置节点为head 他下一个k+1节点 head.next 应该指向k所以上面那句话的意思就是这个
head.next = null; |
同时暂时将下个节点赋值为null 否则会产生环 最终 null是头节点的下一个节点
61. 旋转链表 2021年3月28日
昨天的每日一题 昨天想好了思路 今天写了出来 周末出去玩了2天 没时间写这个.
难度中等530收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置。
示例 1:
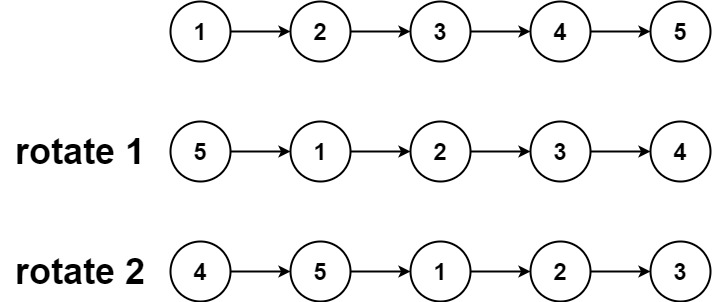
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 |
示例 2:
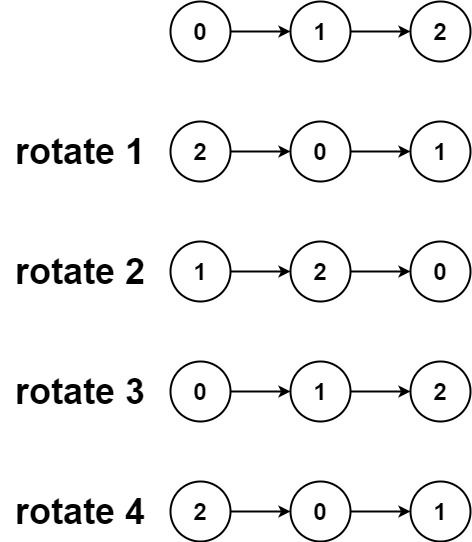
输入:head = [0,1,2], k = 4 |
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 500]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 1000 <= k <= 2 * 109
Java
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) { |
解题思路
这个K次 其实是判断链表在哪个关节处切开 分成2份重新合并的意思,我理解的是这样的,所以先记录下首节点,然后进行一次遍历 算出个数 同时将链表首尾相连变成一个环,然后取模运算找到要被切开的点,最小循环切开返回.
1006. 笨阶乘 2021年4月1日
难度中等119收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
通常,正整数 n 的阶乘是所有小于或等于 n 的正整数的乘积。例如,factorial(10) = 10 * 9 * 8 * 7 * 6 * 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1。
相反,我们设计了一个笨阶乘 clumsy:在整数的递减序列中,我们以一个固定顺序的操作符序列来依次替换原有的乘法操作符:乘法(*),除法(/),加法(+)和减法(-)。
例如,clumsy(10) = 10 * 9 / 8 + 7 - 6 * 5 / 4 + 3 - 2 * 1。然而,这些运算仍然使用通常的算术运算顺序:我们在任何加、减步骤之前执行所有的乘法和除法步骤,并且按从左到右处理乘法和除法步骤。
另外,我们使用的除法是地板除法(floor division),所以 10 * 9 / 8 等于 11。这保证结果是一个整数。
实现上面定义的笨函数:给定一个整数 N,它返回 N 的笨阶乘。
示例 1:
输入:4 |
示例 2:
输入:10 |
提示:
1 <= N <= 10000-2^31 <= answer <= 2^31 - 1(答案保证符合 32 位整数。)
停了好多天了 希望今天开始继续搞起来了
Java
public int clumsy(int N) { |
解题思路
2天没做,思路有点下降了,没有想出来 我想了4分割 然后分别计算 然后求和,问题是约等于会出错,还是考虑不周,学习了栈思路,用加减顺序不重要的特性 先计算*/保存结果在栈中 最后累加. 还是分段式处理.还有另一种解法 数学方法 有点变态要分析 略
面试题 17.21. 直方图的水量 2021年4月2日
难度困难158收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
给定一个直方图(也称柱状图),假设有人从上面源源不断地倒水,最后直方图能存多少水量?直方图的宽度为 1。

上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的直方图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的水(蓝色部分表示水)。 感谢 Marcos 贡献此图。
示例:
输入: [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] |
Java
public int trap(int[] height) { |
解题思路
刚开始正向的想法很难,要记录太多的变量了,后来当作整个图来判断,用完整的方格去减去 溢出的部分,再减去原来存在的部分就是可以容量的部门.


